Tailbone & Coccyx Pain
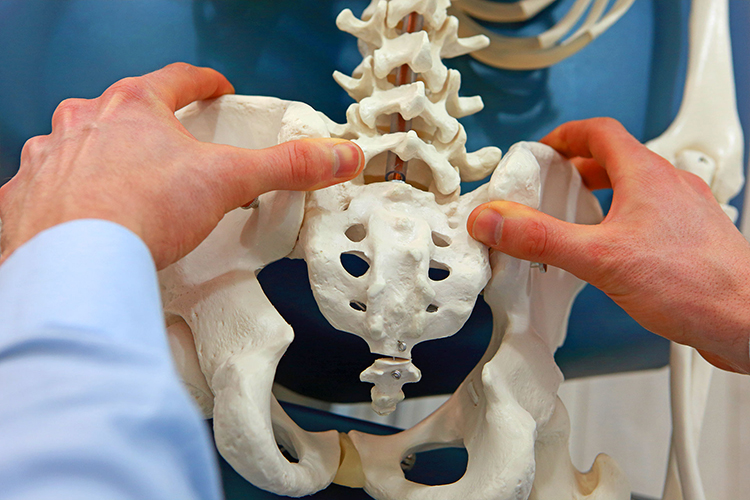
What Is Tailbone & Coccyx Pain?
Tailbone and coccyx pain, medically known as coccydynia, refers to discomfort or aching in the bony structure at the base of the spine. This pain can range from mild to severe and may worsen when sitting, leaning back, or during activities that put pressure on the tailbone. Though it’s often temporary, coccydynia can persist in some cases, requiring medical attention.
What Causes Tailbone & Coccyx Pain?
Tailbone pain can stem from a variety of factors, including:
- Injuries:
- Falls or trauma directly impacting the coccyx.
- Repetitive strain from activities like cycling or rowing.
- Childbirth:
- Pressure or injury to the coccyx during vaginal delivery.
- Prolonged Sitting:
- Sitting on hard or narrow surfaces for extended periods.
- Degenerative Conditions:
- Arthritis affecting the joints near the coccyx.
- Other Causes:
- Infections, such as pilonidal cysts near the tailbone.
- Tumors or growths in the lower spine.
- Idiopathic causes, where no specific reason is identified.
Understanding the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of Tailbone & Coccyx Pain?
Symptoms of coccydynia may include:
- Persistent or sharp pain localized at the base of the spine.
- Discomfort that worsens with sitting or leaning back.
- Pain during activities such as cycling or prolonged standing.
- Tenderness or swelling around the coccyx.
- Radiating pain to the lower back, hips, or legs.
If the pain persists or is accompanied by fever, numbness, or difficulty controlling bowel or bladder function, immediate medical evaluation is necessary.
How Is Tailbone & Coccyx Pain Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
- Medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, recent injuries, and activities that may contribute to the pain.
- Physical examination: They’ll check for tenderness, swelling, or mobility issues in the coccyx area.
- Imaging tests: X-rays or MRIs may be used to identify fractures, arthritis, or other abnormalities.
- Lab tests: These may be conducted if an infection or other systemic condition is suspected.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to determine the best course of treatment.
What Are the Treatment Options for Tailbone & Coccyx Pain?
Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the pain. Common options include:
- Conservative Treatments:
- Using a cushion or donut-shaped pillow to reduce pressure while sitting.
- Applying ice or heat packs to the affected area to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Physical Therapy:
- Stretching and strengthening exercises for the pelvic floor and surrounding muscles.
- Posture correction to reduce strain on the tailbone.
- Injections:
- Corticosteroid, local anesthetic, or biologic injections to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
- Surgical Options:
- Rarely, surgical removal of the coccyx (coccygectomy) may be considered for severe, persistent cases.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Avoiding prolonged sitting or adjusting your seating posture.
When Should You See a Doctor for Tailbone & Coccyx Pain?
You should consult a healthcare provider if:
- The pain persists for more than a few weeks despite home care.
- You experience swelling, redness, or warmth near the coccyx.
- The pain is severe or interferes with daily activities.
- There are additional symptoms, such as fever, numbness, or changes in bowel or bladder control.
Take Control of Tailbone Pain Today
Tailbone and coccyx pain can be frustrating and disruptive, but with the right treatment, relief is possible. If you’re experiencing persistent discomfort, consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and a personalized care plan. Don’t let tailbone pain hold you back—take the first step toward comfort and recovery today!
