Elbow Pain
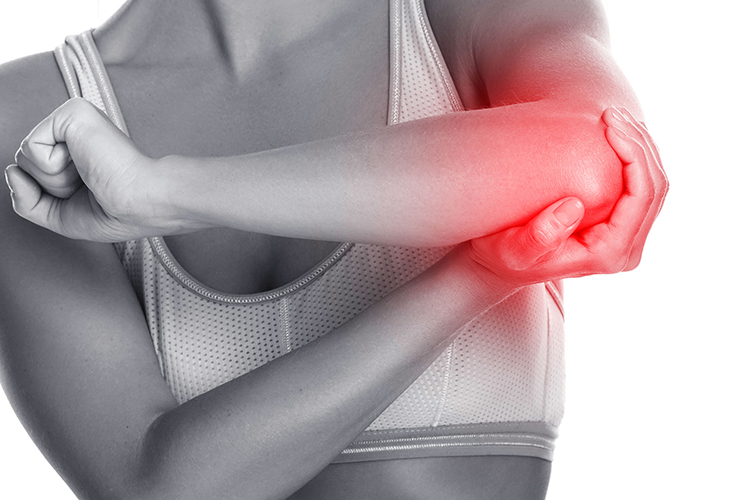

What Is Elbow Pain?
Elbow pain refers to discomfort or stiffness in or around the elbow joint. It can occur suddenly due to an injury or develop gradually because of overuse or underlying medical conditions. This common issue can affect daily activities like lifting, gripping, or even bending the arm.
What Are the Common Causes of Elbow Pain?
Elbow pain can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Injuries:
- Sprains or strains from physical activity.
- Fractures or dislocations caused by trauma.
- Overuse Conditions:
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis): Inflammation of the tendons on the outer part of the elbow.
- Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis): A similar condition affecting the inner part of the elbow.
- Bursitis: Swelling of the fluid-filled sac (bursa) near the elbow joint.
- Medical Conditions:
- Arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Nerve compression, like cubital tunnel syndrome.
- Gout or other types of crystal-induced joint inflammation.
Identifying the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of Elbow Pain?
Elbow pain can present in different ways depending on its cause. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent ache or sharp pain in the elbow or surrounding areas.
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around the joint.
- Weakness or stiffness in the arm.
- Pain that worsens with specific activities, like gripping or lifting.
- Numbness or tingling, particularly with nerve-related conditions.
If the pain is severe or doesn’t improve with rest and basic care, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider.
How Is Elbow Pain Diagnosed?
A thorough diagnosis often involves the following steps:
- Medical history: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, recent activities, and any prior injuries.
- Physical examination: They will assess your range of motion, strength, and areas of tenderness.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds may be used to identify fractures, soft tissue damage, or arthritis.
- Lab tests: For conditions like gout or infection, blood work or fluid sampling may be needed.
Accurate diagnosis is key to developing an effective treatment plan.
What Are the Treatment Options for Elbow Pain?
Treatment for elbow pain depends on its cause and severity. Common approaches include:
- Conservative Treatments:
- Resting the affected arm and avoiding aggravating activities.
- Applying ice or heat to reduce swelling and relieve discomfort.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Wearing a brace or compression sleeve for support.
- Physical Therapy:
- Stretching and strengthening exercises to improve mobility and reduce strain.
- Injections:
- Corticosteroid or biologic injections to reduce inflammation in cases of arthritis or tendonitis.
- Minimally invasive treatment: Percutaneous tenotomy may be considered for cases of medial and lateral epicondylitis
- Surgical Options:
- Surgery may be necessary for severe cases, such as fractures or advanced arthritis.
When Should You See a Doctor for Elbow Pain?
You should seek medical attention if:
- The pain is severe or persists despite home care.
- The elbow appears deformed or swollen after an injury.
- You experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arm.
- There is an inability to move the joint normally.
Find Relief from Elbow Pain Today
Elbow pain can disrupt your routine, but effective treatments are available to help you regain comfort and mobility. If you’re experiencing persistent discomfort or other concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored care plan. Take the first step toward feeling better!
